In this Article we will see the Order management basic flow in Oracle Fusion Cloud
Below diagram presents the overall order-to-cash flow.
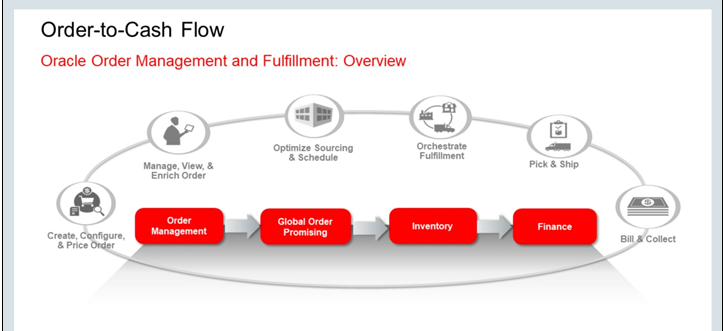
As a first step an order is created or captured in Oracle Order Management Cloud.
The order is priced using Oracle Fusion Pricing.
Products can be configured using Oracle Fusion Configurator.
To help in fulfilling the Order Order entry specialist include useful fulfillment information in the Order.
Oracle Fusion Global Order Promising generates a supply recommendation and schedule.
Oracle Supply Chain Planning Cloud uses the order data in planning for component availability in the case of models and kits.
Order Management Cloud then start the Order orchestration process for order fulfillment, which includes reserving material, sending requests to ship material, sending requests to generate invoices, and billing customers. You can also use various fulfillment methods, such as drop shipment, back-to-back, and internal transfers.
Oracle Fusion Shipping ships the product to the customer.
Oracle Financials Cloud sends the invoices to the customer.
You can use Order Management Cloud to fulfill standard products, services, configurations, models, and kits.
See the below screenshot to understand the flow in more practical way
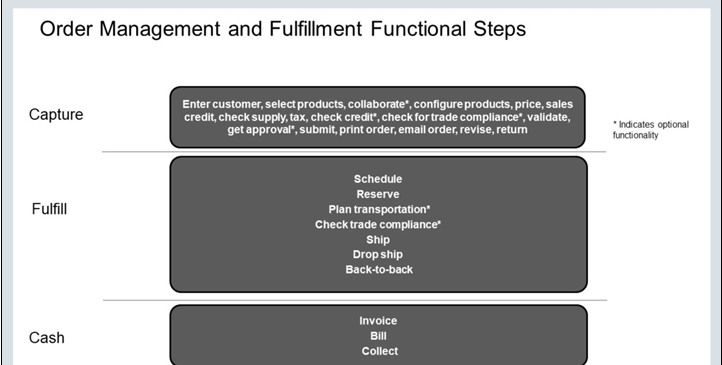
Order Management Cloud is a key solution in the order-to-cash flow. This diagram depicts the different functions of order capture and fulfillment, and the variety of channels that are involved.
Capture orders in any of the following ways:
- From various other sources and channels using Web services.
- Through order import.
- By creating orders directly in Order Management Cloud. It is a manual process where the Order entry specialist enters the Order details . You can configure items, price them, calculate tax, and so on.
Fulfill orders:
- Use the Order user interface to monitor the fulfillment process.
- View statuses of the order lines and the associated orchestration processes.
- Revise orders with carefully controlled and validated changes.
- Define constraints to determine the types of changes that can be made, who makes changes, and when changes are made.
Key
- EDI: Electronic Data Interchange
- POS: Point of Sale
- 3PL: Third-Party Logistics
- WMS: Warehouse Management System
- CM: Contract Manufacturing

